How to Build Internal Apps with ILLA Cloud and FerretDB
In this blog post, we will explore ways to quickly build internal apps in minutes using ILLA Cloud and FerretDB.
FerretDB is an open-source document database replacement that turns PostgreSQL or SQLite into a MongoDB compatible database, using these relational databases as the backend.
By connecting FerretDB with ILLA Cloud, you can use the same MongoDB commands to run queries and create dashboards, admin panels, or internal tools.
Let's get started.
Prerequisites
You can get started with ILLA Cloud by setting your connection URI as the data source. See quickstart guide for more on setting up FerretDB.
Before you proceed, you will need to have the following:
- FerretDB connection URI (e.g.
mongodb://username:password@127.0.0.1:27017/?authMechanism=PLAIN) - ILLA Cloud account
Creating FerretDB resource
We'll use ILLA Builder to create a simple dashboard UI for the FerretDB intance.
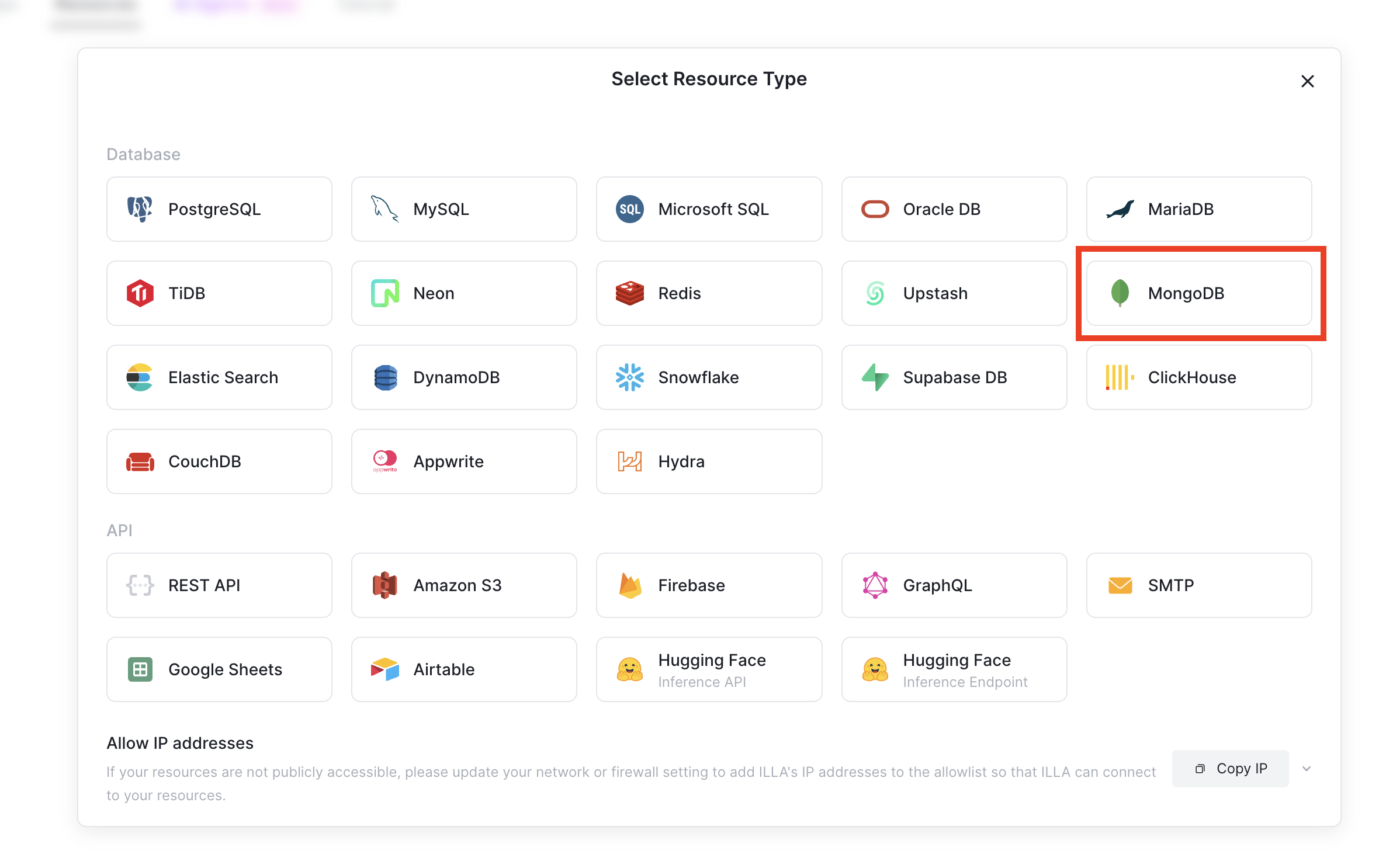
An ILLA resource is a stored configuration for connecting to a data source. This resource exposes your data source so you can run queries on it through ILLA. ILLA provides several resource type connections that you can use, including PostgreSQL, Supabase, and MongoDB.
As a true alternative to MongoDB, FerretDB works with most of the familiar MongoDB tools and applications. So, to create a FerretDB resource for ILLA Builder, connect to your FerretDB instance using the MongoDB resource type.
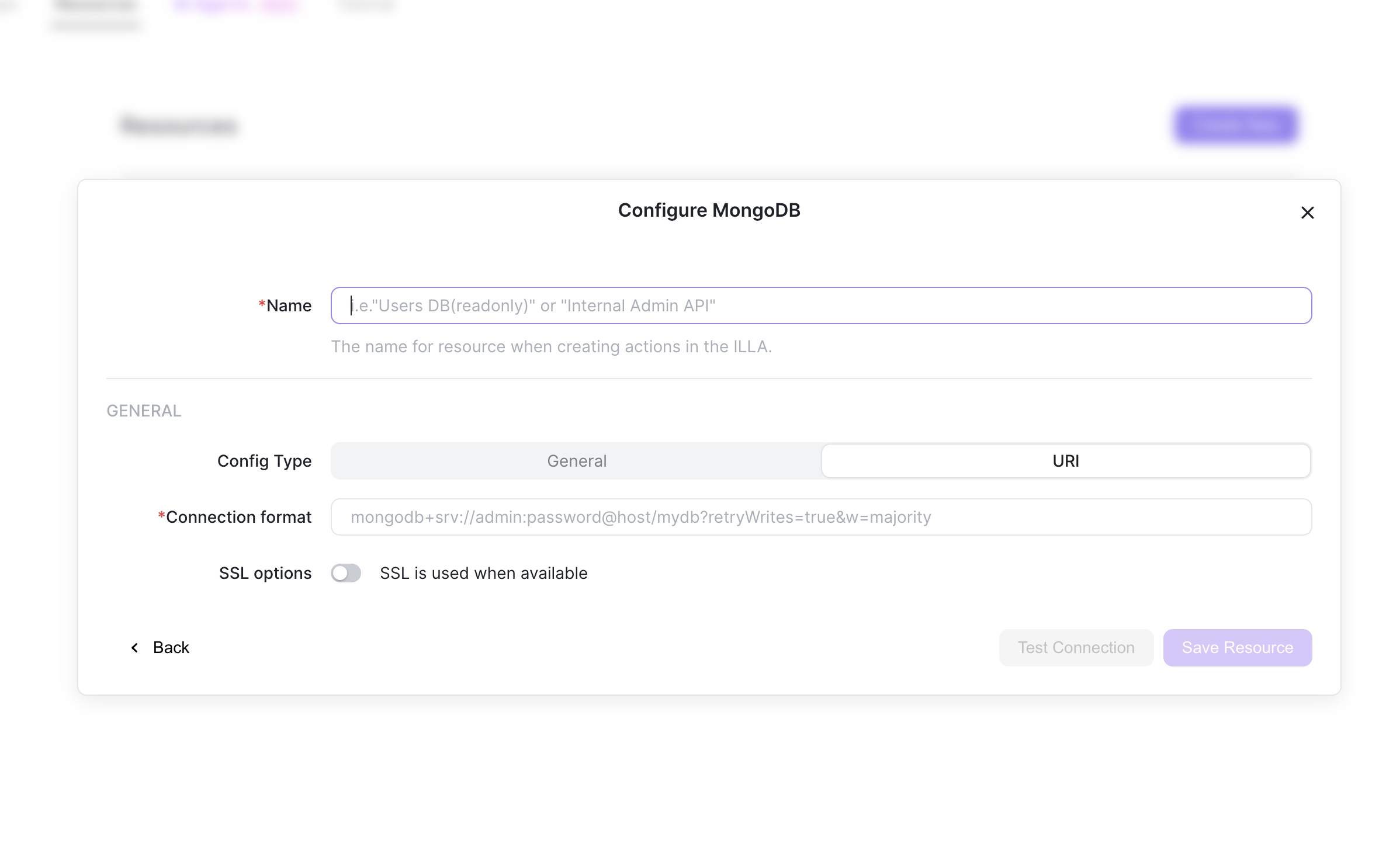
Once it opens the connection window for the resource, set the name of your resource and the connection string URI.
Creating actions in ILLA
Actions in ILLA represent operations to perform on the resources, such as CRUD or aggregation operations. They also connect your data operations to components in ILLA.
From the ILLA Builder, we will create components to interact with our FerretDB instance.
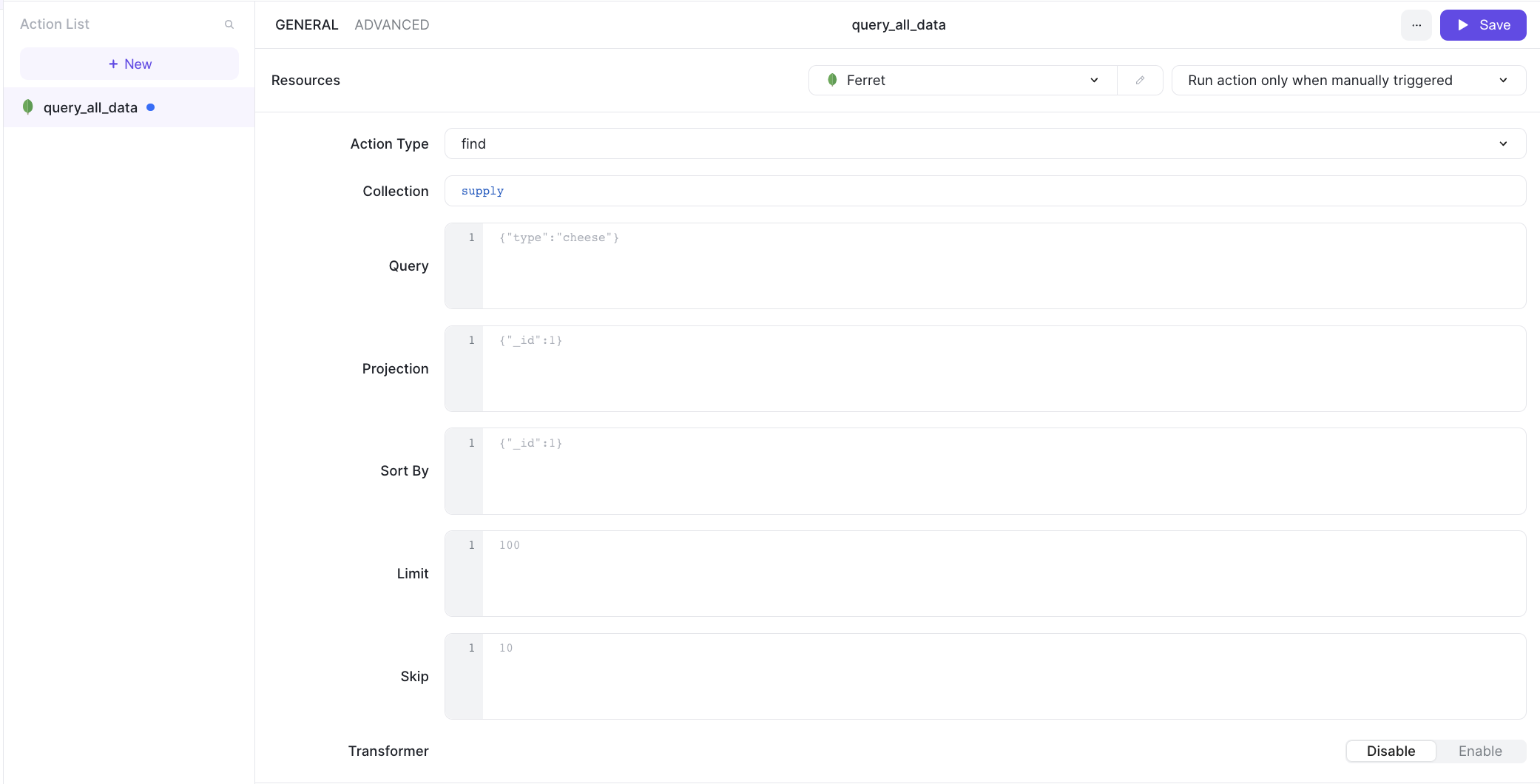
ILLA provides "Action type", "Collection", and "Transformer" methods when creating actions where the Action type represent commands, such as bulkwrite, find, findOne, aggregate, deleteMany, deleteOne, listCollections, and count.
1. Query all data using find
Let's an create action for retrieving all the data in the supply collection of the FerretDB instance.
Then save and run it.
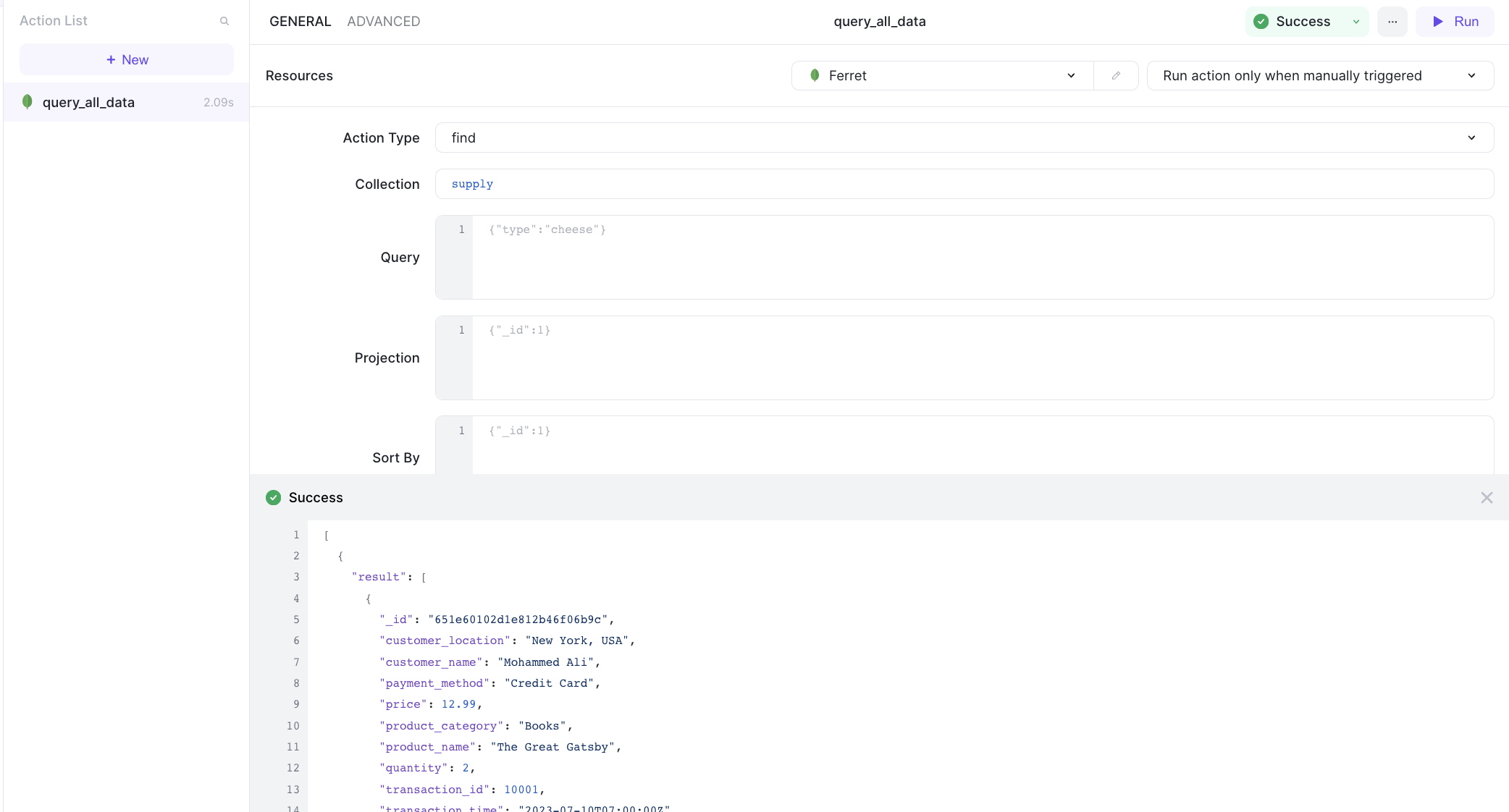
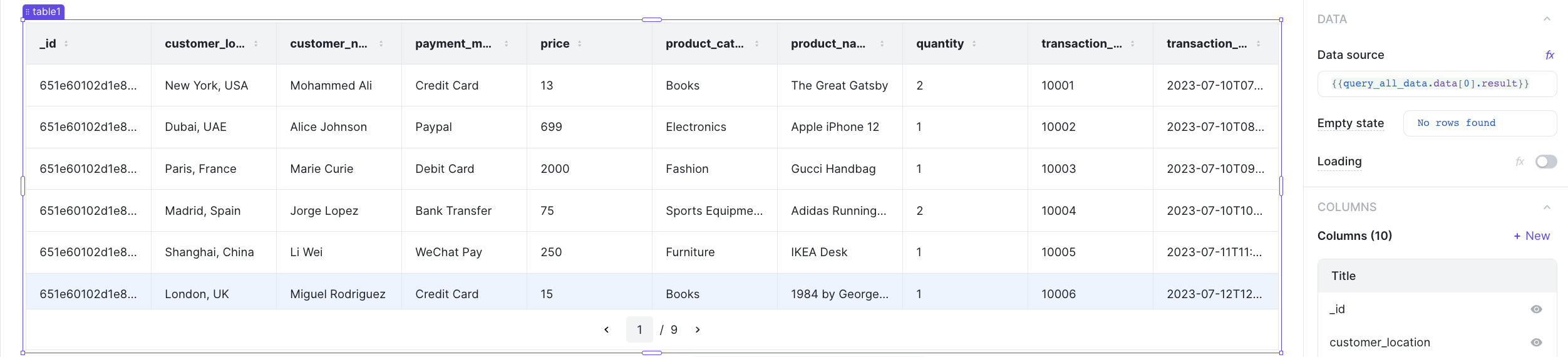
Let's add a table to the page and then connect it to the action.
Update the data source to read the result: {{query_all_data.data[0].result}}.
2. Run aggregation operation
This is an aggregation operation that gets the total number of transactions per location. In ILLA, you can express it as:
[
{
"$group": {
"_id": "$customer_location",
"totalTransactions": { "$sum": 1 }
}
},
{
"$sort": { "totalTransactions": -1 } }
]
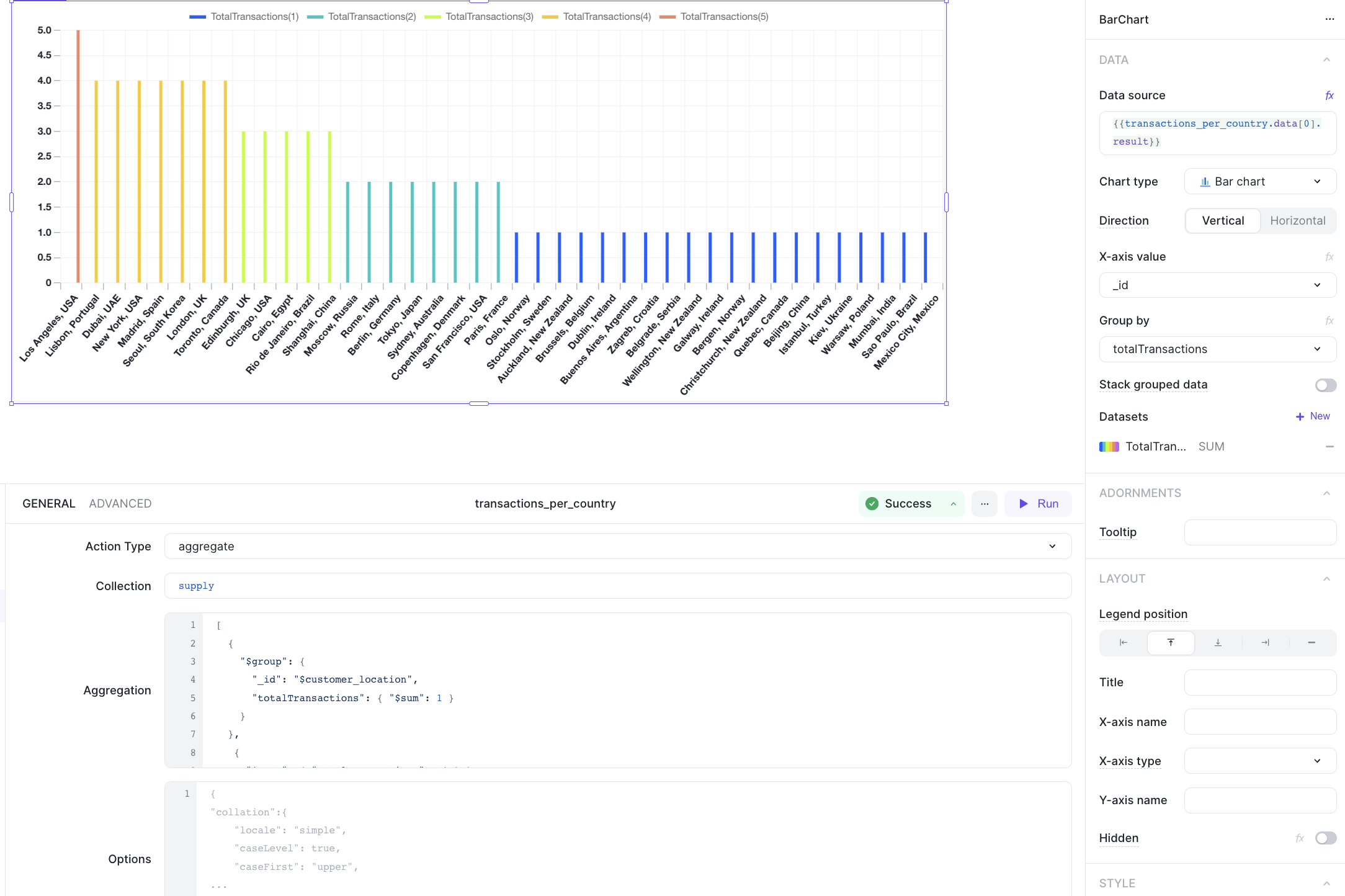
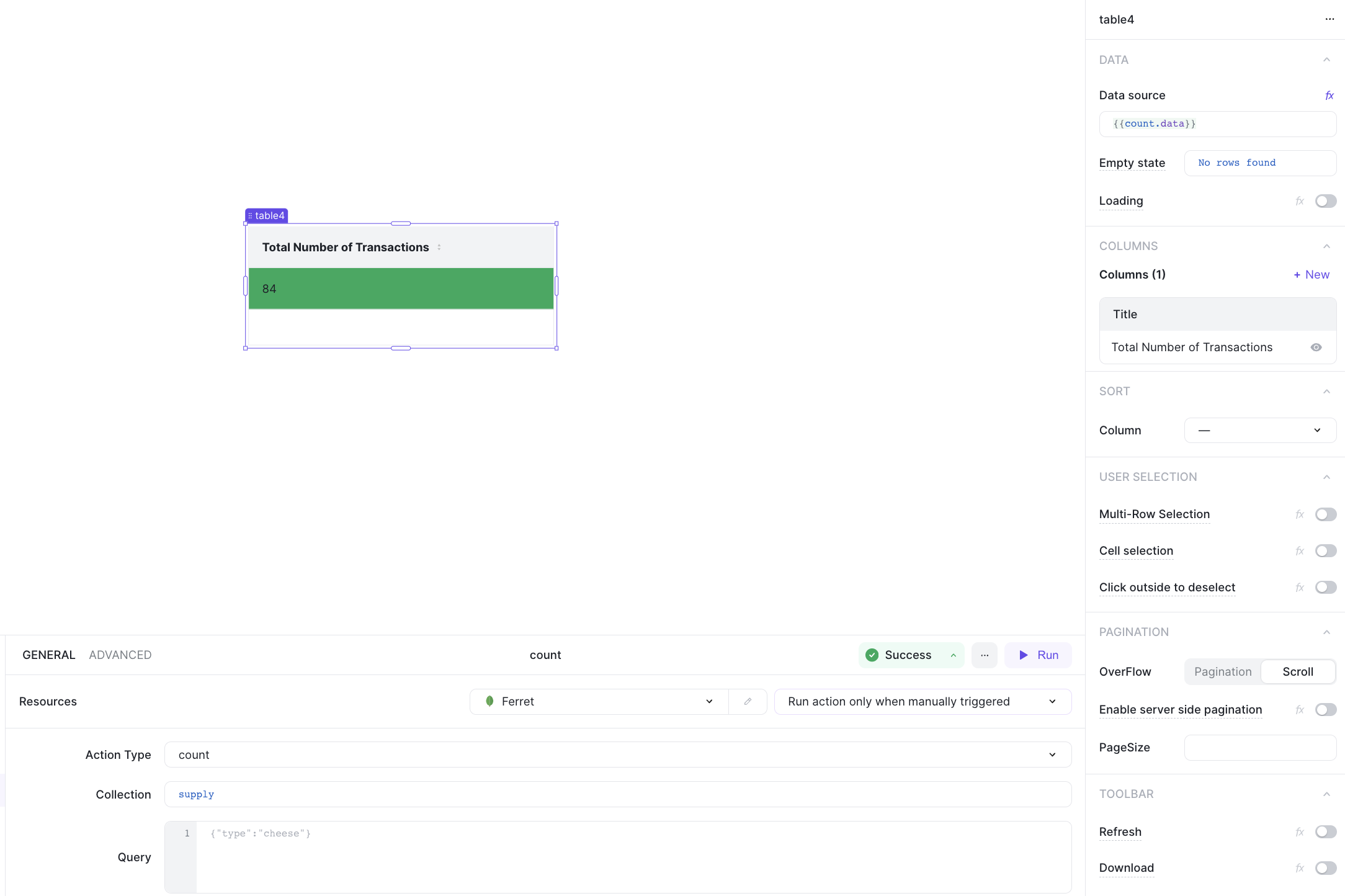
3. Count all documents
Add a table component to visualize the total number of transactions in the collection.
Then use the count command to get the total.
Once that's we can display the result in a table with {{count.data}}
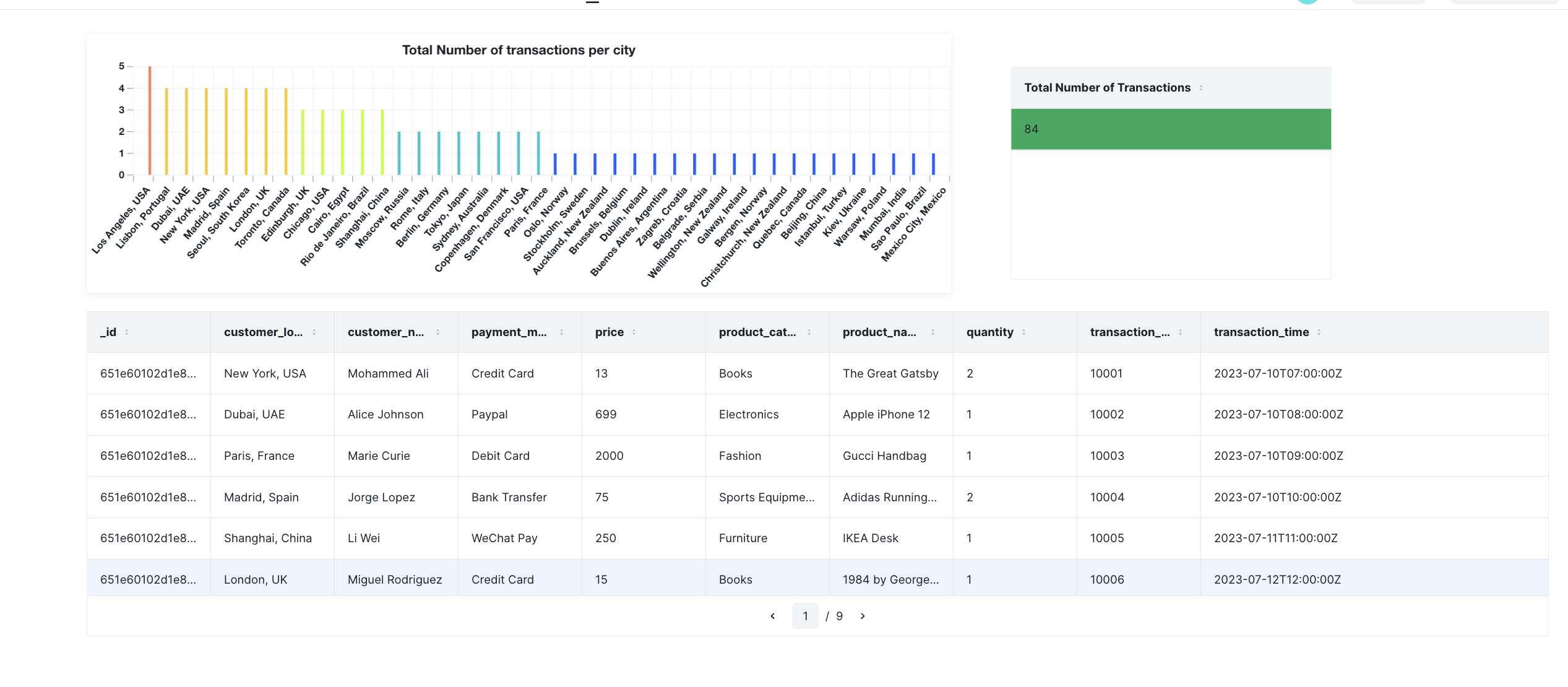
The combined view of the 3 actions should look like this:
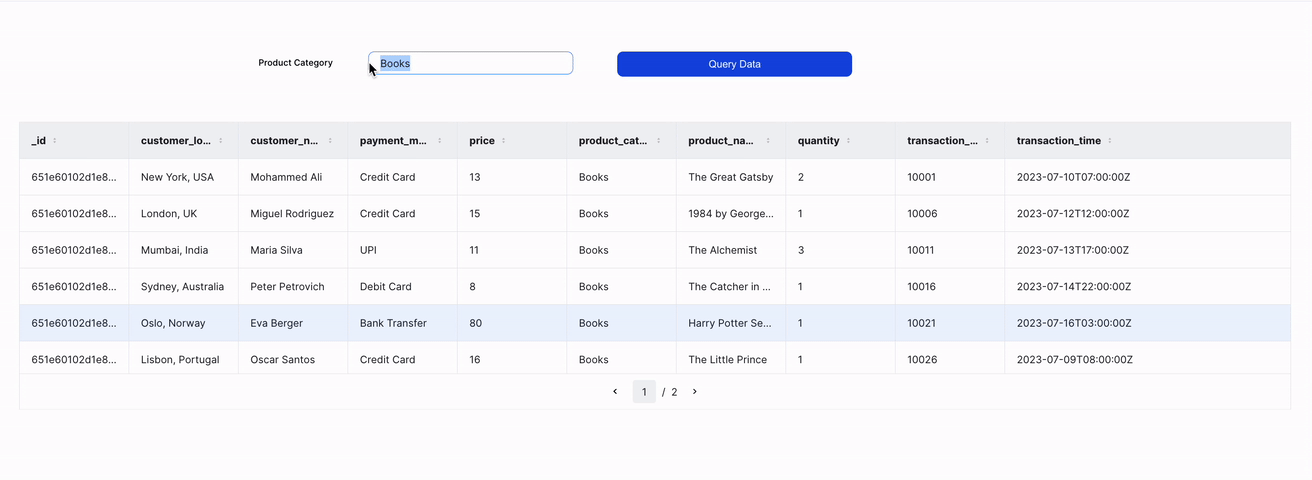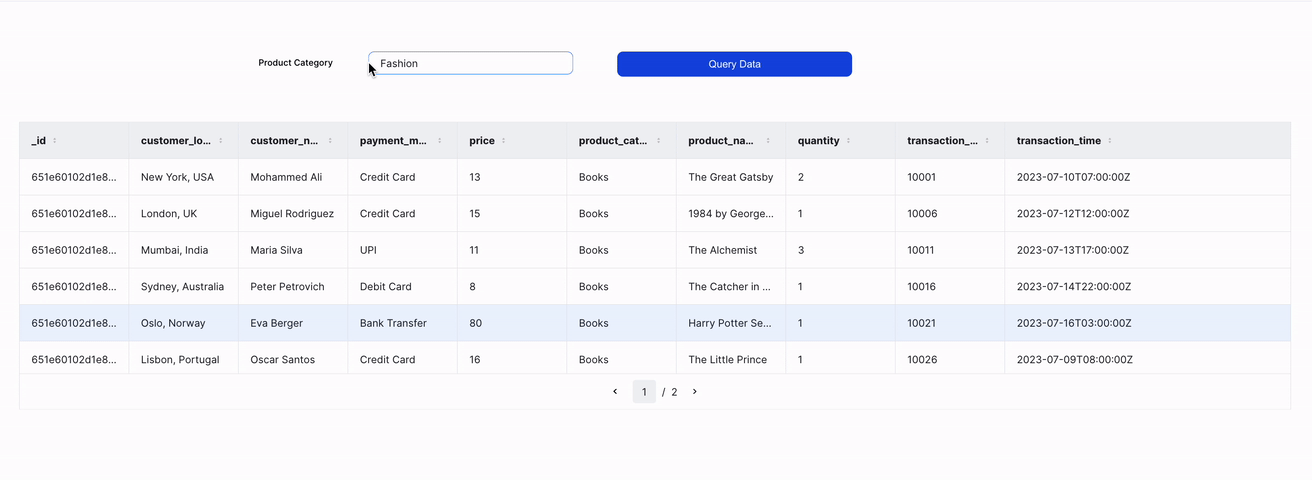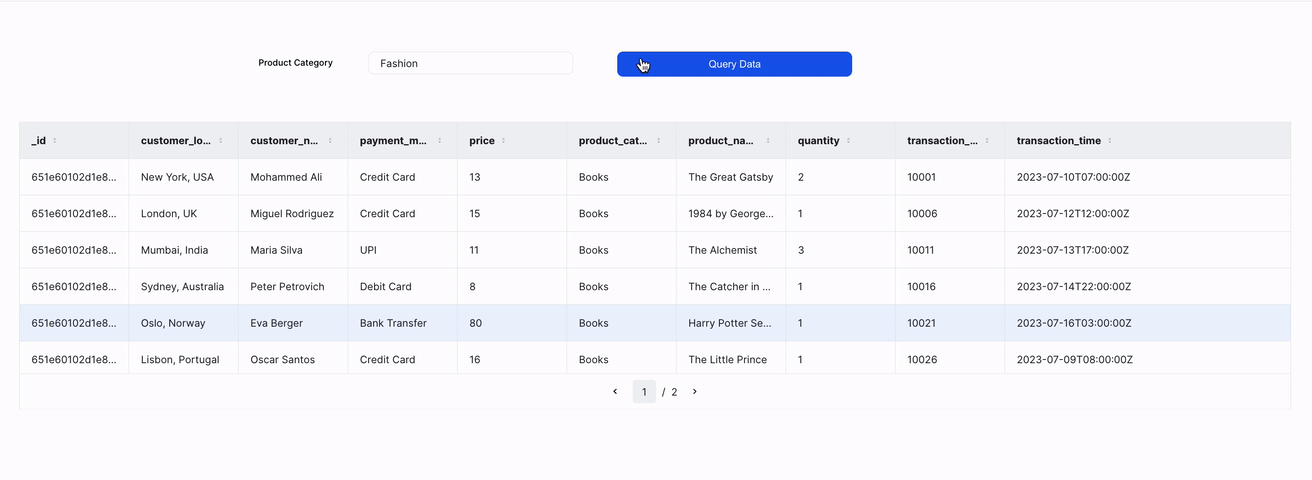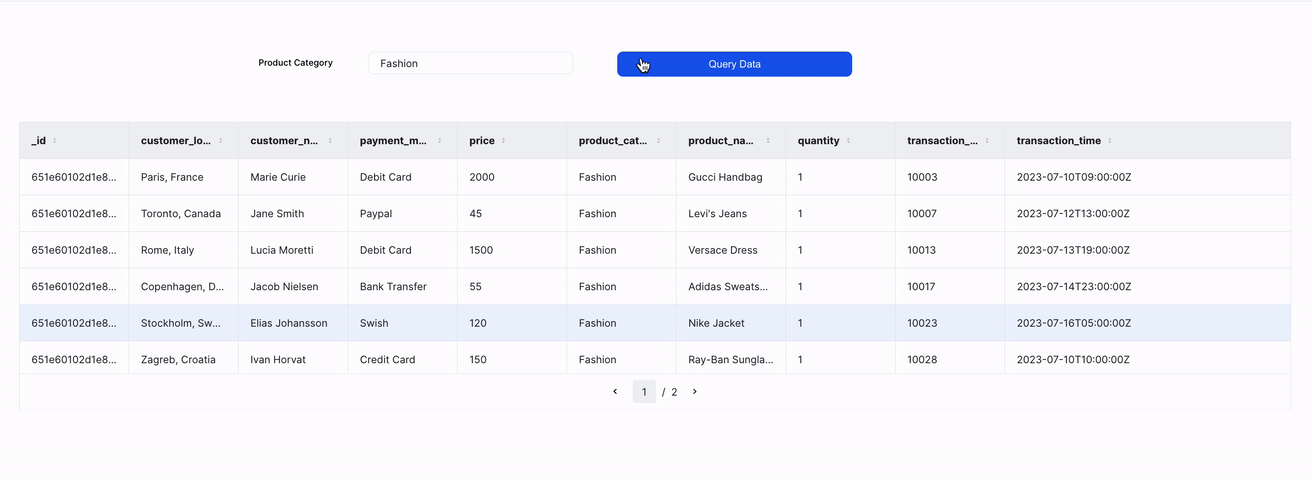
4. Query with input
With ILLA cloud, you can add an input text component to the page and use it's input to query the FerretDB instance.
Start by adding an input and a button component.
Then add a new action that uses the find command to query the collection based on the specified input.
The query for this action is: {"product_category": "{{prod_cat.value}}"}
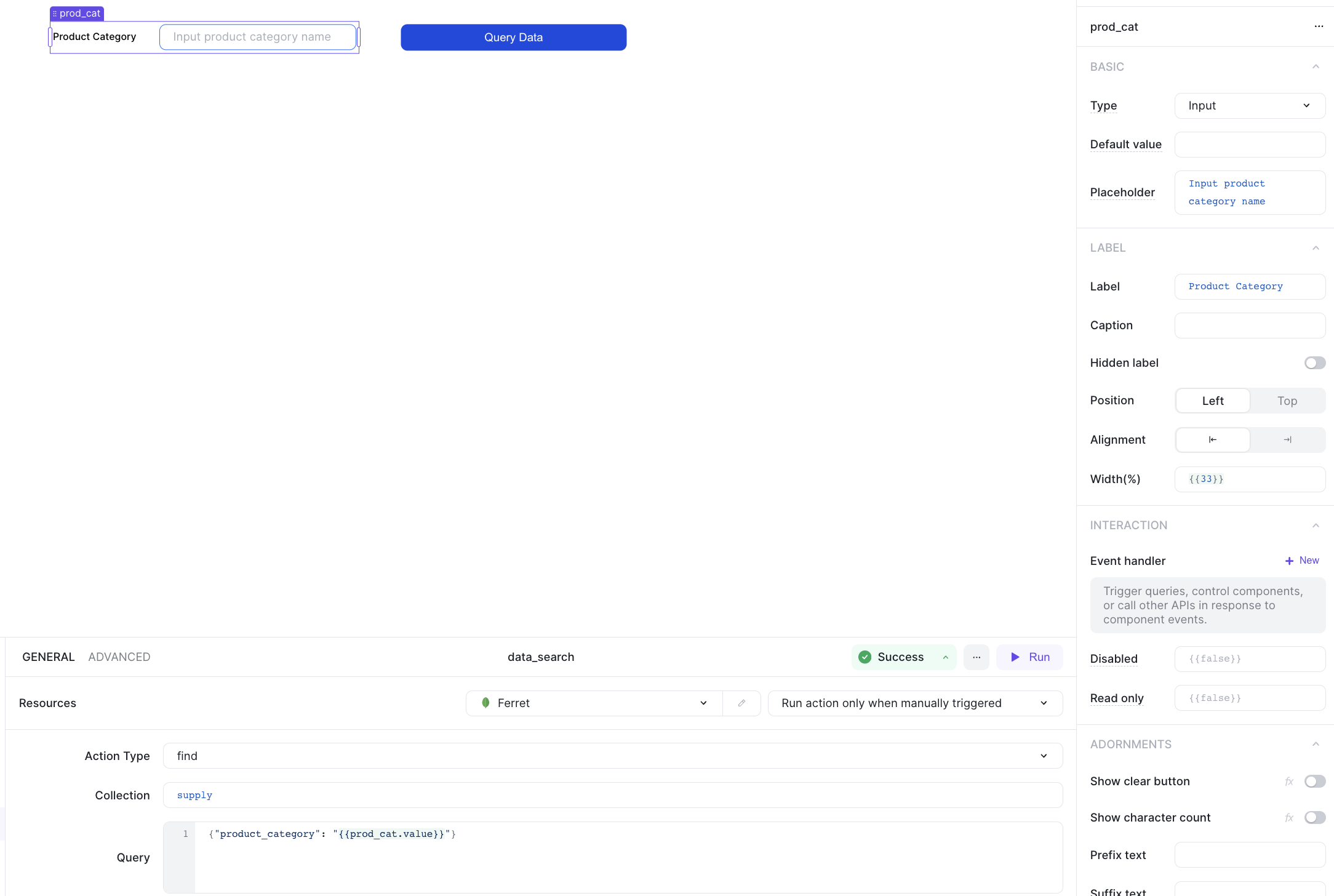
Add a click event handler to the button component and assign the action to it.
Finally, add a table to the screen and set the data source to read the result of the action.
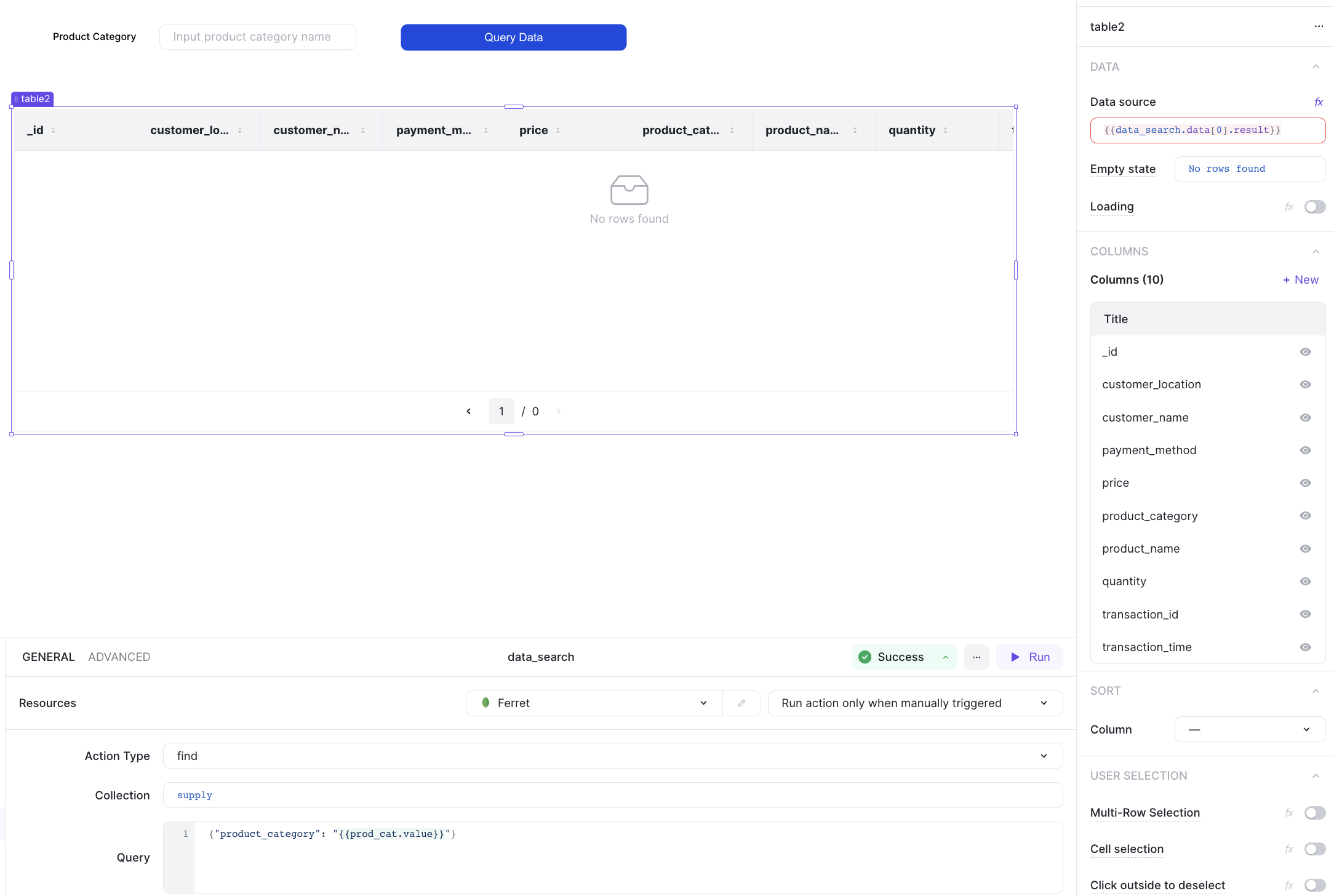
A preview of the UI is shown below:
Start working with FerretDB data on ILLA Cloud
Anyone building on ILLA Cloud can start leveraging FerretDB for their internal apps and admin panels. With ILLA Cloud and FerretDB, you can quickly build your apps in minutes using its numerous out-of-the-box components, drag-and-drop features, and database integrations.
Beyond its open source benefits, FerretDB has a growing community and amazing team ready to help with bugs, feature requests, questions – whatever you need. You can learn more about FerretDB here.
Want to know more about monitoring and visualization of data on FerretDB? See Grafana Monitoring and Visualization for FerretDB.
